| Mar 12, 2022 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Tremendous-absorbent hydrogels will be engineered to soak up important extents of water, in some instances with a swelling ratio as excessive as 3000 occasions their weight in water.
|
|
These polymer gels discover functions that vary from diapers to biomedical use to components that preserve the soil moist for plant development.
|
|
Hydrogels are generally made as macroscopic solids both as cubes or as beads and swell as soon as uncovered to a liquid – a course of which is kind of fast for hydrogel microbeads (&sim 10 seconds) however can take as much as 24 hours for a lot bigger solids corresponding to cubes or cylinders.
|
|
For a big piece of gel to swell quickly, it’s essential to make it porous. The size scale related for diffusion will then be the pore diameter fairly than the general gel measurement. If the pores are microscale and are interconnected, then porous gels can swell at charges which might be 100−1000-fold greater than these of nonporous gels.
|
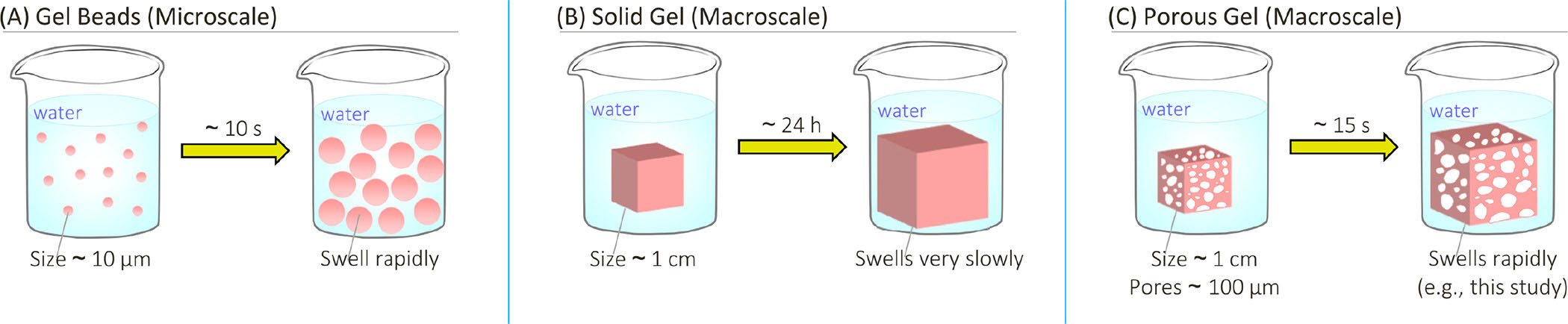 |
| Gel-swelling dynamics at totally different size scales. Dry gels are positioned in water at t = 0 and allowed to swell (develop) to their last measurement. Swelling happens by diffusion of water into the dry gel. (A) Microscale gel beads (∼10 µm measurement) swell in seconds to their last measurement. (B) A stable macroscale gel (∼1 cm measurement) takes ∼24 hours to develop to its last swollen measurement. (C) A macroscale gel with microscale pores expands far more quickly in comparison with (B). On this examine, one such porous gel is proven to develop to 4x its authentic measurement inside 15 seconds. (Reprinted with permission by American Chemical Society)
|
|
If a macroscale hydrogel can develop quickly, its growth could possibly be exploited for doing work, i.e., the chemical power related to gel growth could possibly be transformed into mechanical power.
|
|
This might make them fascinating for utilizing them as synthetic muscle mass: The movement of a increasing and contracting gel will be harvested to carry out mechanical work as an actuator: for example, a cycle of gel growth and contraction (in response to gentle, temperature, or salt) will be coupled to the lifting and decreasing of a weight.
|
|
In a latest paper in ACS Utilized Supplies & Interfaces (“Superfast-Increasing Porous Hydrogels: Pushing New Frontiers in Changing Chemical Potential into Helpful Mechanical Work”), researchers current a brand new strategy that yields porous gels with an unprecedented mixture of fast swelling-expansion charges and excessive swelling extents.
|
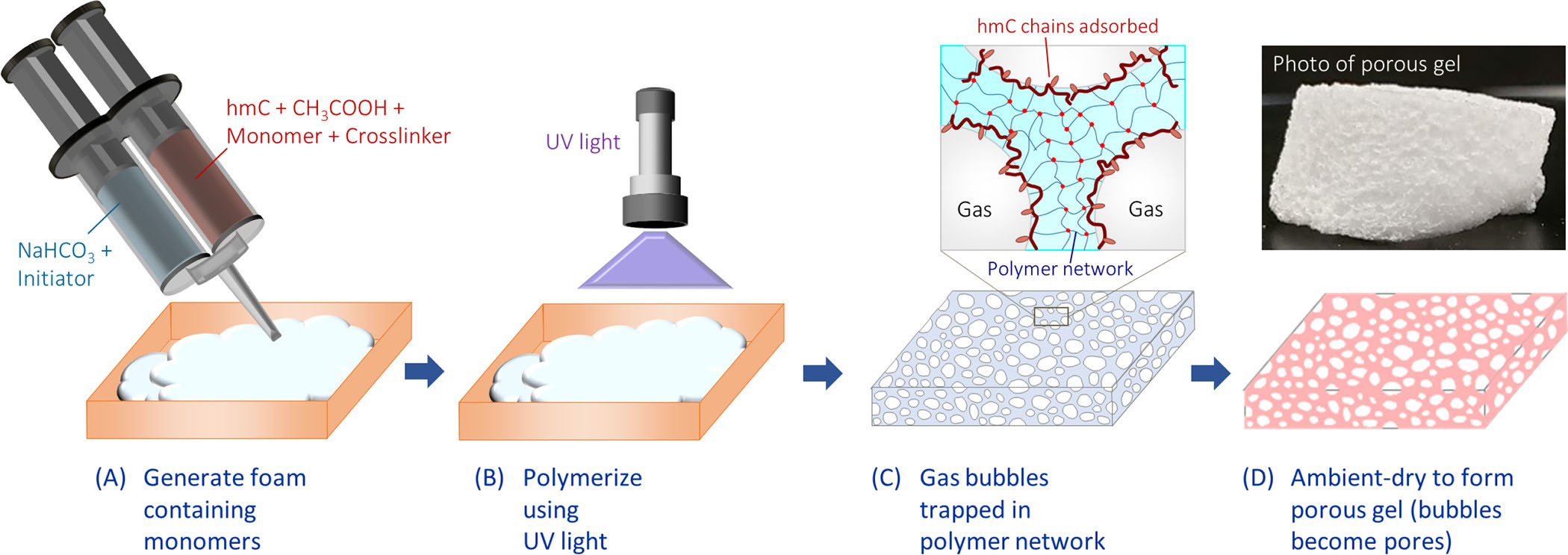 |
| Schematic of the process used to synthesize porous gels. (A) A foam of the monomers is ready utilizing a double-barreled syringe (DBS). One barrel of the DBS is an acidic resolution of monomers, cross-linkers, and the hmC stabilizer, whereas the opposite barrel is a fundamental resolution with the UV initiator. On the mixing tip of the DBS, CO2 gasoline is produced, and bubbles of the gasoline are stabilized by hmC chains. (B) The froth is polymerized by UV gentle for two min. (C) The bubbles within the foam are retained throughout the polymerization whereas a polymer gel community is shaped across the bubbles. (D) The gel is dried underneath ambient situations to present the porous gel. The picture (inset) reveals that the fabric is a strong stable with a sponge-like texture. (Reprinted with permission by American Chemical Society)
|
|
As illustrated above, this novel strategy includes foaming of a monomer resolution by injecting it out of a double-barreled syringe (DBS). The froth is generated in situ through the response of an acid and a base within the two barrels of the DBS, which mix to provide CO2 gasoline within the type of bubbles. The bubbles are stabilized by an amphiphilic biopolymer, hydrophobically modified chitosan (hmC), current in one of many barrels.
|
|
Monomers (acrylamide and acrylic acid, with cross-linkers) within the foam are then polymerized to kind a gel across the bubbles. Subsequently, this gel is dried underneath ambient situations to present a porous stable with a porosity >90% and a pore measurement round 200 µm.
|
|
When this dry gel is added to water, it absorbs water quickly till an equilibrium is achieved in 15 seconds at about 300x its weight. The hydrogels can then be shrunk by lowering the pH, including salt, or including ethanol.
|
|
The swollen gel is strong sufficient to be picked up by hand. Reversible growth−contraction cycles, the place the gel expands by absorbing 100x water after which contracts by expelling 100x water, will be accomplished in about 60 seconds.
|
|
The authors report that they’ve used gel growth to raise hundreds in opposition to gravity. A 40 mg gel is ready to carry out &sim0.42 mJ of labor over 40 seconds, which interprets into an influence density of 260 mW/kg.
|
|
The researchers conclude that this skill to harness the chemical potential of the gel to do helpful mechanical work could possibly be a sport changer for a lot of functions, together with within the creation of synthetic muscle mass.
|



