[ad_1]
Overview
On this put up, we’ll evaluate three superior strategies for bettering the efficiency and generalization energy of recurrent neural networks. By the top of the part, you’ll know most of what there’s to find out about utilizing recurrent networks with Keras. We’ll reveal all three ideas on a temperature-forecasting drawback, the place you might have entry to a time sequence of information factors coming from sensors put in on the roof of a constructing, reminiscent of temperature, air stress, and humidity, which you utilize to foretell what the temperature might be 24 hours after the final information level. It is a pretty difficult drawback that exemplifies many frequent difficulties encountered when working with time sequence.
We’ll cowl the next strategies:
- Recurrent dropout — It is a particular, built-in method to make use of dropout to battle overfitting in recurrent layers.
- Stacking recurrent layers — This will increase the representational energy of the community (at the price of greater computational hundreds).
- Bidirectional recurrent layers — These current the identical info to a recurrent community in numerous methods, rising accuracy and mitigating forgetting points.
A temperature-forecasting drawback
Till now, the one sequence information we’ve coated has been textual content information, such because the IMDB dataset and the Reuters dataset. However sequence information is discovered in lots of extra issues than simply language processing. In all of the examples on this part, you’ll play with a climate timeseries dataset recorded on the Climate Station on the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry in Jena, Germany.
On this dataset, 14 completely different portions (such air temperature, atmospheric stress, humidity, wind course, and so forth) have been recorded each 10 minutes, over a number of years. The unique information goes again to 2003, however this instance is proscribed to information from 2009–2016. This dataset is ideal for studying to work with numerical time sequence. You’ll use it to construct a mannequin that takes as enter some information from the latest previous (a number of days’ value of information factors) and predicts the air temperature 24 hours sooner or later.
Obtain and uncompress the info as follows:
dir.create("~/Downloads/jena_climate", recursive = TRUE)
obtain.file(
"https://s3.amazonaws.com/keras-datasets/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip",
"~/Downloads/jena_climate/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip"
)
unzip(
"~/Downloads/jena_climate/jena_climate_2009_2016.csv.zip",
exdir = "~/Downloads/jena_climate"
)
Let’s have a look at the info.
Observations: 420,551
Variables: 15
$ `Date Time` <chr> "01.01.2009 00:10:00", "01.01.2009 00:20:00", "...
$ `p (mbar)` <dbl> 996.52, 996.57, 996.53, 996.51, 996.51, 996.50,...
$ `T (degC)` <dbl> -8.02, -8.41, -8.51, -8.31, -8.27, -8.05, -7.62...
$ `Tpot (Ok)` <dbl> 265.40, 265.01, 264.91, 265.12, 265.15, 265.38,...
$ `Tdew (degC)` <dbl> -8.90, -9.28, -9.31, -9.07, -9.04, -8.78, -8.30...
$ `rh (%)` <dbl> 93.3, 93.4, 93.9, 94.2, 94.1, 94.4, 94.8, 94.4,...
$ `VPmax (mbar)` <dbl> 3.33, 3.23, 3.21, 3.26, 3.27, 3.33, 3.44, 3.44,...
$ `VPact (mbar)` <dbl> 3.11, 3.02, 3.01, 3.07, 3.08, 3.14, 3.26, 3.25,...
$ `VPdef (mbar)` <dbl> 0.22, 0.21, 0.20, 0.19, 0.19, 0.19, 0.18, 0.19,...
$ `sh (g/kg)` <dbl> 1.94, 1.89, 1.88, 1.92, 1.92, 1.96, 2.04, 2.03,...
$ `H2OC (mmol/mol)` <dbl> 3.12, 3.03, 3.02, 3.08, 3.09, 3.15, 3.27, 3.26,...
$ `rho (g/m**3)` <dbl> 1307.75, 1309.80, 1310.24, 1309.19, 1309.00, 13...
$ `wv (m/s)` <dbl> 1.03, 0.72, 0.19, 0.34, 0.32, 0.21, 0.18, 0.19,...
$ `max. wv (m/s)` <dbl> 1.75, 1.50, 0.63, 0.50, 0.63, 0.63, 0.63, 0.50,...
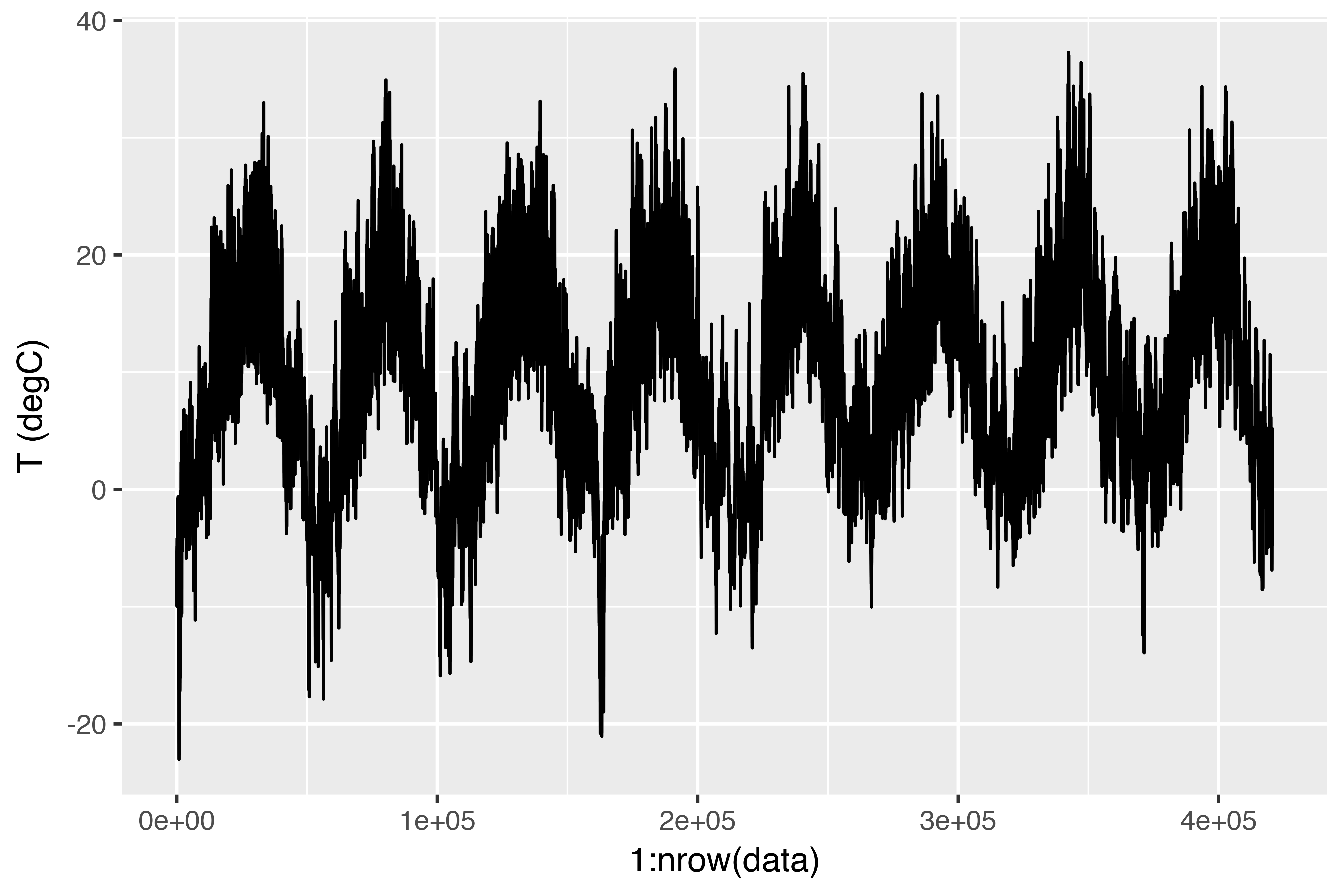
$ `wd (deg)` <dbl> 152.3, 136.1, 171.6, 198.0, 214.3, 192.7, 166.5...Right here is the plot of temperature (in levels Celsius) over time. On this plot, you’ll be able to clearly see the yearly periodicity of temperature.

Here’s a extra slender plot of the primary 10 days of temperature information (see determine 6.15). As a result of the info is recorded each 10 minutes, you get 144 information factors per day.
ggplot(information[1:1440,], aes(x = 1:1440, y = `T (degC)`)) + geom_line()

On this plot, you’ll be able to see each day periodicity, particularly evident for the final 4 days. Additionally notice that this 10-day interval should be coming from a reasonably chilly winter month.
If you happen to have been attempting to foretell common temperature for the following month given a number of months of previous information, the issue could be simple, as a result of dependable year-scale periodicity of the info. However wanting on the information over a scale of days, the temperature seems to be much more chaotic. Is that this time sequence predictable at a each day scale? Let’s discover out.
Making ready the info
The precise formulation of the issue might be as follows: given information going way back to lookback timesteps (a timestep is 10 minutes) and sampled each steps timesteps, can you expect the temperature in delay timesteps? You’ll use the next parameter values:
lookback = 1440— Observations will return 10 days.steps = 6— Observations might be sampled at one information level per hour.delay = 144— Targets might be 24 hours sooner or later.
To get began, it is advisable do two issues:
- Preprocess the info to a format a neural community can ingest. That is simple: the info is already numerical, so that you don’t have to do any vectorization. However every time sequence within the information is on a special scale (for instance, temperature is usually between -20 and +30, however atmospheric stress, measured in mbar, is round 1,000). You’ll normalize every time sequence independently in order that all of them take small values on the same scale.
- Write a generator operate that takes the present array of float information and yields batches of information from the latest previous, together with a goal temperature sooner or later. As a result of the samples within the dataset are extremely redundant (pattern N and pattern N + 1 may have most of their timesteps in frequent), it could be wasteful to explicitly allocate each pattern. As an alternative, you’ll generate the samples on the fly utilizing the unique information.
NOTE: Understanding generator features
A generator operate is a particular kind of operate that you just name repeatedly to acquire a sequence of values from. Typically turbines want to take care of inner state, so they’re usually constructed by calling one other one more operate which returns the generator operate (the surroundings of the operate which returns the generator is then used to trace state).
For instance, the sequence_generator() operate under returns a generator operate that yields an infinite sequence of numbers:
sequence_generator <- operate(begin) {
worth <- begin - 1
operate() {
worth <<- worth + 1
worth
}
}
gen <- sequence_generator(10)
gen()
[1] 10[1] 11The present state of the generator is the worth variable that’s outlined exterior of the operate. Observe that superassignment (<<-) is used to replace this state from inside the operate.
Generator features can sign completion by returning the worth NULL. Nevertheless, generator features handed to Keras coaching strategies (e.g. fit_generator()) ought to at all times return values infinitely (the variety of calls to the generator operate is managed by the epochs and steps_per_epoch parameters).
First, you’ll convert the R information body which we learn earlier right into a matrix of floating level values (we’ll discard the primary column which included a textual content timestamp):
You’ll then preprocess the info by subtracting the imply of every time sequence and dividing by the usual deviation. You’re going to make use of the primary 200,000 timesteps as coaching information, so compute the imply and customary deviation for normalization solely on this fraction of the info.
The code for the info generator you’ll use is under. It yields a listing (samples, targets), the place samples is one batch of enter information and targets is the corresponding array of goal temperatures. It takes the next arguments:
information— The unique array of floating-point information, which you normalized in itemizing 6.32.lookback— What number of timesteps again the enter information ought to go.delay— What number of timesteps sooner or later the goal must be.min_indexandmax_index— Indices within theinformationarray that delimit which timesteps to attract from. That is helpful for holding a section of the info for validation and one other for testing.shuffle— Whether or not to shuffle the samples or draw them in chronological order.batch_size— The variety of samples per batch.step— The interval, in timesteps, at which you pattern information. You’ll set it 6 so as to draw one information level each hour.
generator <- operate(information, lookback, delay, min_index, max_index,
shuffle = FALSE, batch_size = 128, step = 6) {
if (is.null(max_index))
max_index <- nrow(information) - delay - 1
i <- min_index + lookback
operate() {
if (shuffle) {
rows <- pattern(c((min_index+lookback):max_index), dimension = batch_size)
} else {
if (i + batch_size >= max_index)
i <<- min_index + lookback
rows <- c(i:min(i+batch_size-1, max_index))
i <<- i + size(rows)
}
samples <- array(0, dim = c(size(rows),
lookback / step,
dim(information)[[-1]]))
targets <- array(0, dim = c(size(rows)))
for (j in 1:size(rows)) {
indices <- seq(rows[[j]] - lookback, rows[[j]]-1,
size.out = dim(samples)[[2]])
samples[j,,] <- information[indices,]
targets[[j]] <- information[rows[[j]] + delay,2]
}
record(samples, targets)
}
}
The i variable accommodates the state that tracks subsequent window of information to return, so it’s up to date utilizing superassignment (e.g. i <<- i + size(rows)).
Now, let’s use the summary generator operate to instantiate three turbines: one for coaching, one for validation, and one for testing. Every will have a look at completely different temporal segments of the unique information: the coaching generator seems to be on the first 200,000 timesteps, the validation generator seems to be on the following 100,000, and the check generator seems to be on the the rest.
lookback <- 1440
step <- 6
delay <- 144
batch_size <- 128
train_gen <- generator(
information,
lookback = lookback,
delay = delay,
min_index = 1,
max_index = 200000,
shuffle = TRUE,
step = step,
batch_size = batch_size
)
val_gen = generator(
information,
lookback = lookback,
delay = delay,
min_index = 200001,
max_index = 300000,
step = step,
batch_size = batch_size
)
test_gen <- generator(
information,
lookback = lookback,
delay = delay,
min_index = 300001,
max_index = NULL,
step = step,
batch_size = batch_size
)
# What number of steps to attract from val_gen so as to see the complete validation set
val_steps <- (300000 - 200001 - lookback) / batch_size
# What number of steps to attract from test_gen so as to see the complete check set
test_steps <- (nrow(information) - 300001 - lookback) / batch_size
A standard-sense, non-machine-learning baseline
Earlier than you begin utilizing black-box deep-learning fashions to unravel the temperature-prediction drawback, let’s attempt a easy, common sense method. It’ll function a sanity verify, and it’ll set up a baseline that you just’ll need to beat so as to reveal the usefulness of more-advanced machine-learning fashions. Such common sense baselines will be helpful whenever you’re approaching a brand new drawback for which there isn’t a recognized answer (but). A traditional instance is that of unbalanced classification duties, the place some lessons are way more frequent than others. In case your dataset accommodates 90% situations of sophistication A and 10% situations of sophistication B, then a common sense method to the classification process is to at all times predict “A” when offered with a brand new pattern. Such a classifier is 90% correct total, and any learning-based method ought to subsequently beat this 90% rating so as to reveal usefulness. Generally, such elementary baselines can show surprisingly laborious to beat.
On this case, the temperature time sequence can safely be assumed to be steady (the temperatures tomorrow are more likely to be near the temperatures right this moment) in addition to periodical with a each day interval. Thus a common sense method is to at all times predict that the temperature 24 hours from now might be equal to the temperature proper now. Let’s consider this method, utilizing the imply absolute error (MAE) metric:
Right here’s the analysis loop.
This yields an MAE of 0.29. As a result of the temperature information has been normalized to be centered on 0 and have an ordinary deviation of 1, this quantity isn’t instantly interpretable. It interprets to a median absolute error of 0.29 x temperature_std levels Celsius: 2.57˚C.
celsius_mae <- 0.29 * std[[2]]
That’s a pretty big common absolute error. Now the sport is to make use of your information of deep studying to do higher.
A fundamental machine-learning method
In the identical method that it’s helpful to ascertain a common sense baseline earlier than attempting machine-learning approaches, it’s helpful to attempt easy, low-cost machine-learning fashions (reminiscent of small, densely related networks) earlier than wanting into difficult and computationally costly fashions reminiscent of RNNs. That is one of the best ways to ensure any additional complexity you throw on the drawback is reliable and delivers actual advantages.
The next itemizing reveals a totally related mannequin that begins by flattening the info after which runs it by way of two dense layers. Observe the shortage of activation operate on the final dense layer, which is typical for a regression drawback. You employ MAE because the loss. Since you consider on the very same information and with the very same metric you probably did with the commonsense method, the outcomes might be straight comparable.
library(keras)
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_flatten(input_shape = c(lookback / step, dim(information)[-1])) %>%
layer_dense(models = 32, activation = "relu") %>%
layer_dense(models = 1)
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
loss = "mae"
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% fit_generator(
train_gen,
steps_per_epoch = 500,
epochs = 20,
validation_data = val_gen,
validation_steps = val_steps
)
Let’s show the loss curves for validation and coaching.

A number of the validation losses are near the no-learning baseline, however not reliably. This goes to indicate the advantage of getting this baseline within the first place: it seems to be not simple to outperform. Your frequent sense accommodates loads of helpful info {that a} machine-learning mannequin doesn’t have entry to.
You could surprise, if a easy, well-performing mannequin exists to go from the info to the targets (the commonsense baseline), why doesn’t the mannequin you’re coaching discover it and enhance on it? As a result of this straightforward answer isn’t what your coaching setup is in search of. The area of fashions by which you’re trying to find an answer – that’s, your speculation area – is the area of all doable two-layer networks with the configuration you outlined. These networks are already pretty difficult. If you’re in search of an answer with an area of difficult fashions, the straightforward, well-performing baseline could also be unlearnable, even when it’s technically a part of the speculation area. That may be a fairly vital limitation of machine studying generally: except the educational algorithm is hardcoded to search for a particular sort of easy mannequin, parameter studying can typically fail to discover a easy answer to a easy drawback.
A primary recurrent baseline
The primary absolutely related method didn’t do nicely, however that doesn’t imply machine studying isn’t relevant to this drawback. The earlier method first flattened the time sequence, which eliminated the notion of time from the enter information. Let’s as an alternative have a look at the info as what it’s: a sequence, the place causality and order matter. You’ll attempt a recurrent-sequence processing mannequin – it must be the proper match for such sequence information, exactly as a result of it exploits the temporal ordering of information factors, in contrast to the primary method.
As an alternative of the LSTM layer launched within the earlier part, you’ll use the GRU layer, developed by Chung et al. in 2014. Gated recurrent unit (GRU) layers work utilizing the identical precept as LSTM, however they’re considerably streamlined and thus cheaper to run (though they could not have as a lot representational energy as LSTM). This trade-off between computational expensiveness and representational energy is seen in all places in machine studying.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_gru(models = 32, input_shape = record(NULL, dim(information)[[-1]])) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1)
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
loss = "mae"
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% fit_generator(
train_gen,
steps_per_epoch = 500,
epochs = 20,
validation_data = val_gen,
validation_steps = val_steps
)
The outcomes are plotted under. A lot better! You possibly can considerably beat the commonsense baseline, demonstrating the worth of machine studying in addition to the prevalence of recurrent networks in comparison with sequence-flattening dense networks on this kind of process.

The brand new validation MAE of ~0.265 (earlier than you begin considerably overfitting) interprets to a imply absolute error of two.35˚C after denormalization. That’s a strong achieve on the preliminary error of two.57˚C, however you most likely nonetheless have a little bit of a margin for enchancment.
Utilizing recurrent dropout to battle overfitting
It’s evident from the coaching and validation curves that the mannequin is overfitting: the coaching and validation losses begin to diverge significantly after a number of epochs. You’re already acquainted with a traditional method for combating this phenomenon: dropout, which randomly zeros out enter models of a layer so as to break happenstance correlations within the coaching information that the layer is uncovered to. However methods to appropriately apply dropout in recurrent networks isn’t a trivial query. It has lengthy been recognized that making use of dropout earlier than a recurrent layer hinders studying quite than serving to with regularization. In 2015, Yarin Gal, as a part of his PhD thesis on Bayesian deep studying, decided the correct method to make use of dropout with a recurrent community: the identical dropout masks (the identical sample of dropped models) must be utilized at each timestep, as an alternative of a dropout masks that varies randomly from timestep to timestep. What’s extra, so as to regularize the representations fashioned by the recurrent gates of layers reminiscent of layer_gru and layer_lstm, a temporally fixed dropout masks must be utilized to the inside recurrent activations of the layer (a recurrent dropout masks). Utilizing the identical dropout masks at each timestep permits the community to correctly propagate its studying error by way of time; a temporally random dropout masks would disrupt this error sign and be dangerous to the educational course of.
Yarin Gal did his analysis utilizing Keras and helped construct this mechanism straight into Keras recurrent layers. Each recurrent layer in Keras has two dropout-related arguments: dropout, a float specifying the dropout fee for enter models of the layer, and recurrent_dropout, specifying the dropout fee of the recurrent models. Let’s add dropout and recurrent dropout to the layer_gru and see how doing so impacts overfitting. As a result of networks being regularized with dropout at all times take longer to totally converge, you’ll practice the community for twice as many epochs.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_gru(models = 32, dropout = 0.2, recurrent_dropout = 0.2,
input_shape = record(NULL, dim(information)[[-1]])) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1)
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
loss = "mae"
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% fit_generator(
train_gen,
steps_per_epoch = 500,
epochs = 40,
validation_data = val_gen,
validation_steps = val_steps
)
The plot under reveals the outcomes. Success! You’re now not overfitting in the course of the first 20 epochs. However though you might have extra secure analysis scores, your finest scores aren’t a lot decrease than they have been beforehand.

Stacking recurrent layers
Since you’re now not overfitting however appear to have hit a efficiency bottleneck, it is best to take into account rising the capability of the community. Recall the outline of the common machine-learning workflow: it’s usually a good suggestion to extend the capability of your community till overfitting turns into the first impediment (assuming you’re already taking fundamental steps to mitigate overfitting, reminiscent of utilizing dropout). So long as you aren’t overfitting too badly, you’re possible underneath capability.
Rising community capability is usually performed by rising the variety of models within the layers or including extra layers. Recurrent layer stacking is a traditional option to construct more-powerful recurrent networks: as an example, what at present powers the Google Translate algorithm is a stack of seven giant LSTM layers – that’s large.
To stack recurrent layers on prime of one another in Keras, all intermediate layers ought to return their full sequence of outputs (a 3D tensor) quite than their output on the final timestep. That is performed by specifying return_sequences = TRUE.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_gru(models = 32,
dropout = 0.1,
recurrent_dropout = 0.5,
return_sequences = TRUE,
input_shape = record(NULL, dim(information)[[-1]])) %>%
layer_gru(models = 64, activation = "relu",
dropout = 0.1,
recurrent_dropout = 0.5) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1)
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
loss = "mae"
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% fit_generator(
train_gen,
steps_per_epoch = 500,
epochs = 40,
validation_data = val_gen,
validation_steps = val_steps
)
The determine under reveals the outcomes. You possibly can see that the added layer does enhance the outcomes a bit, although not considerably. You possibly can draw two conclusions:
- Since you’re nonetheless not overfitting too badly, you may safely improve the scale of your layers in a quest for validation-loss enchancment. This has a non-negligible computational price, although.
- Including a layer didn’t assist by a major issue, so it’s possible you’ll be seeing diminishing returns from rising community capability at this level.

Utilizing bidirectional RNNs
The final method launched on this part is known as bidirectional RNNs. A bidirectional RNN is a standard RNN variant that may supply higher efficiency than an everyday RNN on sure duties. It’s regularly utilized in natural-language processing – you may name it the Swiss Military knife of deep studying for natural-language processing.
RNNs are notably order dependent, or time dependent: they course of the timesteps of their enter sequences so as, and shuffling or reversing the timesteps can utterly change the representations the RNN extracts from the sequence. That is exactly the explanation they carry out nicely on issues the place order is significant, such because the temperature-forecasting drawback. A bidirectional RNN exploits the order sensitivity of RNNs: it consists of utilizing two common RNNs, such because the layer_gru and layer_lstm you’re already acquainted with, every of which processes the enter sequence in a single course (chronologically and antichronologically), after which merging their representations. By processing a sequence each methods, a bidirectional RNN can catch patterns which may be ignored by a unidirectional RNN.
Remarkably, the truth that the RNN layers on this part have processed sequences in chronological order (older timesteps first) might have been an arbitrary resolution. No less than, it’s a choice we made no try to query up to now. Might the RNNs have carried out nicely sufficient in the event that they processed enter sequences in antichronological order, as an example (newer timesteps first)? Let’s do that in apply and see what occurs. All it is advisable do is write a variant of the info generator the place the enter sequences are reverted alongside the time dimension (change the final line with record(samples[,ncol(samples):1,], targets)). Coaching the identical one-GRU-layer community that you just used within the first experiment on this part, you get the outcomes proven under.

The reversed-order GRU underperforms even the commonsense baseline, indicating that on this case, chronological processing is essential to the success of your method. This makes excellent sense: the underlying GRU layer will usually be higher at remembering the latest previous than the distant previous, and naturally the more moderen climate information factors are extra predictive than older information factors for the issue (that’s what makes the commonsense baseline pretty sturdy). Thus the chronological model of the layer is sure to outperform the reversed-order model. Importantly, this isn’t true for a lot of different issues, together with pure language: intuitively, the significance of a phrase in understanding a sentence isn’t normally depending on its place within the sentence. Let’s attempt the identical trick on the LSTM IMDB instance from part 6.2.
library(keras)
# Variety of phrases to think about as options
max_features <- 10000
# Cuts off texts after this variety of phrases
maxlen <- 500
imdb <- dataset_imdb(num_words = max_features)
c(c(x_train, y_train), c(x_test, y_test)) %<-% imdb
# Reverses sequences
x_train <- lapply(x_train, rev)
x_test <- lapply(x_test, rev)
# Pads sequences
x_train <- pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen = maxlen) <4>
x_test <- pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen = maxlen)
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_embedding(input_dim = max_features, output_dim = 128) %>%
layer_lstm(models = 32) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1, activation = "sigmoid")
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = "rmsprop",
loss = "binary_crossentropy",
metrics = c("acc")
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% match(
x_train, y_train,
epochs = 10,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2
)You get efficiency almost equivalent to that of the chronological-order LSTM. Remarkably, on such a textual content dataset, reversed-order processing works simply in addition to chronological processing, confirming the speculation that, though phrase order does matter in understanding language, which order you utilize isn’t essential. Importantly, an RNN skilled on reversed sequences will study completely different representations than one skilled on the unique sequences, a lot as you’d have completely different psychological fashions if time flowed backward in the true world – in the event you lived a life the place you died in your first day and have been born in your final day. In machine studying, representations which are completely different but helpful are at all times value exploiting, and the extra they differ, the higher: they provide a unique approach from which to take a look at your information, capturing points of the info that have been missed by different approaches, and thus they will help enhance efficiency on a process. That is the instinct behind ensembling, an idea we’ll discover in chapter 7.
A bidirectional RNN exploits this concept to enhance on the efficiency of chronological-order RNNs. It seems to be at its enter sequence each methods, acquiring doubtlessly richer representations and capturing patterns that will have been missed by the chronological-order model alone.

To instantiate a bidirectional RNN in Keras, you utilize the bidirectional() operate, which takes a recurrent layer occasion as an argument. The bidirectional() operate creates a second, separate occasion of this recurrent layer and makes use of one occasion for processing the enter sequences in chronological order and the opposite occasion for processing the enter sequences in reversed order. Let’s attempt it on the IMDB sentiment-analysis process.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
layer_embedding(input_dim = max_features, output_dim = 32) %>%
bidirectional(
layer_lstm(models = 32)
) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1, activation = "sigmoid")
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = "rmsprop",
loss = "binary_crossentropy",
metrics = c("acc")
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% match(
x_train, y_train,
epochs = 10,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2
)
It performs barely higher than the common LSTM you tried within the earlier part, reaching over 89% validation accuracy. It additionally appears to overfit extra shortly, which is unsurprising as a result of a bidirectional layer has twice as many parameters as a chronological LSTM. With some regularization, the bidirectional method would possible be a robust performer on this process.
Now let’s attempt the identical method on the temperature prediction process.
mannequin <- keras_model_sequential() %>%
bidirectional(
layer_gru(models = 32), input_shape = record(NULL, dim(information)[[-1]])
) %>%
layer_dense(models = 1)
mannequin %>% compile(
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
loss = "mae"
)
historical past <- mannequin %>% fit_generator(
train_gen,
steps_per_epoch = 500,
epochs = 40,
validation_data = val_gen,
validation_steps = val_steps
)
This performs about in addition to the common layer_gru. It’s simple to know why: all of the predictive capability should come from the chronological half of the community, as a result of the antichronological half is understood to be severely underperforming on this process (once more, as a result of the latest previous issues way more than the distant previous on this case).
Going even additional
There are lots of different issues you may attempt, so as to enhance efficiency on the temperature-forecasting drawback:
- Regulate the variety of models in every recurrent layer within the stacked setup. The present selections are largely arbitrary and thus most likely suboptimal.
- Regulate the educational fee utilized by the
RMSpropoptimizer. - Strive utilizing
layer_lstmas an alternative oflayer_gru. - Strive utilizing an even bigger densely related regressor on prime of the recurrent layers: that’s, an even bigger dense layer or perhaps a stack of dense layers.
- Don’t overlook to finally run the best-performing fashions (when it comes to validation MAE) on the check set! In any other case, you’ll develop architectures which are overfitting to the validation set.
As at all times, deep studying is extra an artwork than a science. We are able to present tips that counsel what’s more likely to work or not work on a given drawback, however, finally, each drawback is exclusive; you’ll have to guage completely different methods empirically. There may be at present no principle that can inform you upfront exactly what it is best to do to optimally clear up an issue. You should iterate.
Wrapping up
Right here’s what it is best to take away from this part:
- As you first realized in chapter 4, when approaching a brand new drawback, it’s good to first set up common sense baselines to your metric of alternative. If you happen to don’t have a baseline to beat, you’ll be able to’t inform whether or not you’re making actual progress.
- Strive easy fashions earlier than costly ones, to justify the extra expense. Generally a easy mannequin will change into your only option.
- When you might have information the place temporal ordering issues, recurrent networks are a fantastic match and simply outperform fashions that first flatten the temporal information.
- To make use of dropout with recurrent networks, it is best to use a time-constant dropout masks and recurrent dropout masks. These are constructed into Keras recurrent layers, so all it’s a must to do is use the
dropoutandrecurrent_dropoutarguments of recurrent layers. - Stacked RNNs present extra representational energy than a single RNN layer. They’re additionally way more costly and thus not at all times value it. Though they provide clear positive factors on complicated issues (reminiscent of machine translation), they could not at all times be related to smaller, less complicated issues.
- Bidirectional RNNs, which have a look at a sequence each methods, are helpful on natural-language processing issues. However they aren’t sturdy performers on sequence information the place the latest previous is way more informative than the start of the sequence.
NOTE: Markets and machine studying
Some readers are sure to wish to take the strategies we’ve launched right here and check out them on the issue of forecasting the long run value of securities on the inventory market (or foreign money alternate charges, and so forth). Markets have very completely different statistical traits than pure phenomena reminiscent of climate patterns. Attempting to make use of machine studying to beat markets, whenever you solely have entry to publicly out there information, is a tough endeavor, and also you’re more likely to waste your time and sources with nothing to indicate for it.
All the time do not forget that with regards to markets, previous efficiency is not an excellent predictor of future returns – wanting within the rear-view mirror is a nasty option to drive. Machine studying, alternatively, is relevant to datasets the place the previous is an excellent predictor of the long run.
[ad_2]